Introduction 🚀
In the age of data-driven decision-making, Snowflake has risen to become one of the most sought-after cloud data platforms, with job listings demanding Snowflake expertise skyrocketing by over 100% in the last two years. If you’re preparing for a role in cloud data engineering, analytics, or development, chances are your interviewer will test your knowledge of Snowflake.
But what exactly do they ask? And more importantly, how do you answer with clarity and confidence? 🤔
In this post, we’ve curated 50 essential Snowflake interview questions and answers that cut through the fluff and focus on what truly matters—real-world applications, best practices, and clear understanding of Snowflake’s architecture and features. Whether you’re a beginner brushing up or a seasoned pro sharpening your edge, this guide will give you the clarity and confidence to stand out in interviews. 💡✅
Snowflake Interview Questions Part1- Fundamentals
1. What is Snowflake?
Snowflake is a fully managed cloud-based data platform that provides data warehousing, data lakes, and data sharing capabilities. Unlike traditional databases, it separates compute and storage, allowing scalability and performance optimization.
2. What key features make Snowflake stand out as a data platform?
Snowflake stands out as a modern data platform due to its innovative architecture and powerful features. One of its most notable strengths is the separation of storage and compute, which allows users to scale each independently based on performance or cost needs.
It supports deployment across multiple cloud providers—AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud—offering flexibility and resilience. Snowflake handles high concurrency with ease through automatic scaling, making it ideal for large organizations with multiple simultaneous users.
Its zero-maintenance design eliminates the need for manual tuning, backups, or infrastructure management. Snowflake also enables secure and real-time data sharing across different accounts and organizations without duplicating data.
Additionally, it natively supports semi-structured data formats like JSON, Parquet, and Avro using standard SQL, simplifying data integration. Features like Time Travel and Fail-safe provide strong capabilities for data recovery and auditing, making Snowflake a robust, enterprise-ready solution for modern data warehousing and analytics.
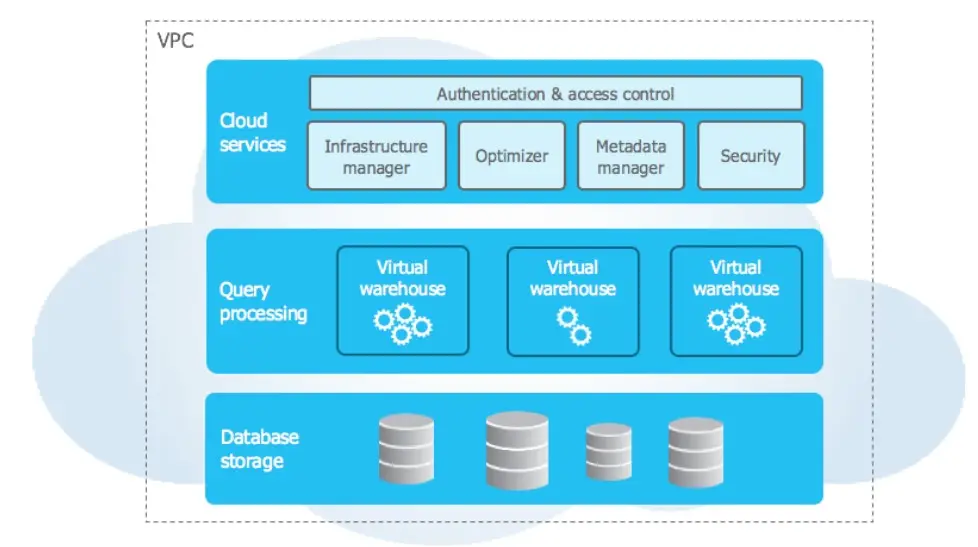
3. Can you explain Snowflake's architecture?
The Snowflake architecture is divided into three layers:
Database Storage Layer
In this layer, Snowflake stores both structured and semi-structured data. The data is automatically compressed, encrypted, and divided into micro-partitions to optimize storage usage and significantly enhance query performance. Snowflake fully manages this layer, so users don’t need to worry about indexing or partitioning.
Compute Layer (Virtual Warehouses)
This layer is responsible for executing all data processing tasks. It consists of one or more independent compute clusters, also known as virtual warehouses. Each warehouse operates in isolation, meaning workloads running on one cluster do not impact the performance of others. This design ensures seamless concurrency and workload isolation.
Cloud Services Layer
Acting as the control center of the platform, this layer includes services such as infrastructure management, metadata handling, query optimization, and security. It coordinates all interactions between users and the system, ensuring that Snowflake remains a fully managed and user-friendly service.
4 - What cloud providers does Snowflake support?
Snowflake supports the following major cloud providers:
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Microsoft Azure
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
This multi-cloud support allows customers to choose their preferred cloud provider and even operate across multiple clouds for flexibility, high availability, and disaster recovery.
5 - What are micro-partitions in Snowflake, and how do they help improve data storage efficiency?
In Snowflake, data is automatically broken down into small chunks called micro-partitions. These chunks are organized in a smart way so that Snowflake can quickly find and read only the parts it needs when you run a query. This saves time and computer power. The data in each micro-partition is also compressed to take up less space, which makes storage more efficient. You don’t have to do anything—Snowflake handles all of it for you in the background.
6 - What is a virtual warehouse?
A compute cluster that processes queries and loads. It can be scaled independently and paused to save costs.
7 - How do virtual warehouses in Snowflake impact data processing in terms of scalability, performance, and cost?
In Snowflake, virtual warehouses are the compute engines that do all the work—like running queries, loading data, or transforming it. You can scale them up (make them more powerful) for faster performance or scale them out (add more warehouses) to handle many users or tasks at the same time. Since each warehouse works separately, they don’t slow each other down. You also only pay for the time a warehouse is running, which helps you manage costs better. This flexibility makes it easy to balance speed, workload, and budget based on your needs.
Below is a comparison of Virtual Warehouses in Snowflake vs. Traditional Compute Resources.
| Feature | Virtual Warehouses (Snowflake) | Traditional Compute Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | Instantly scalable (up or out) as needed | Limited, manual scaling; may require hardware upgrades |
| Resource Sharing | Independent; multiple warehouses can run without interference | Shared resources can cause performance bottlenecks |
| Cost Management | Pay only for usage (per second billing when active) | Pay for allocated resources whether used or not |
| Setup & Maintenance | Fully managed by Snowflake; no tuning or setup needed | Requires manual setup, tuning, and ongoing maintenance |
| Performance Handling | High concurrency; workloads don’t affect each other | Performance can degrade under heavy loads |
| Flexibility | Easily resized or paused anytime | Changes often require planning and downtime |
| Automation | Auto-suspend/resume, auto-scaling | Mostly manual processes |
8 - How does Snowflake ensure data security?
Snowflake ensures data security through a combination of built-in features and best practices. It encrypts all data—both when it’s stored (at rest) and when it’s being used or moved (in transit). It also offers role-based access control, so only authorized users can view or change specific data. Snowflake supports multi-factor authentication (MFA) and can integrate with external identity providers like Okta or Azure AD. On top of that, it provides network security features like IP whitelisting and private connectivity options. For even higher protection, Snowflake offers enterprise-level security features like data masking, row-level security, and support for compliance standards such as HIPAA, SOC 2, and GDPR.
Key Points to Remember
End-to-end encryption
Role-based access control
Support for multi-factor authentication (MFA) and network policies
9 - Explain Snowflake's always-on encryption feature?
Always-on encryption in Snowflake means that all your data is automatically encrypted at all times—whether it’s being stored (at rest), moved (in transit), or even temporarily processed.
You don’t have to turn it on or manage keys manually—Snowflake handles everything behind the scenes using strong encryption standards (like AES-256). This ensures your data stays secure and protected from unauthorized access at every stage, without adding complexity for users or admins. It’s a key part of Snowflake’s built-in data security.
10 - What is the Time Travel feature in Snowflake, and how does it help users?
Snowflake’s Time Travel lets users view or restore data from the past—up to 1 to 90 days, depending on your plan. This is helpful if data was accidentally deleted or changed, or if you need to audit or compare historical data. It makes recovering lost information easy without needing a full backup
11 - What is Fail-safe and how it differs from Time Travel?
Time Travel lets you access or restore data that was deleted or changed within a set period (up to 90 days, depending on your plan). It’s great for undoing mistakes or checking past versions of your data—and you can do it yourself using SQL.
Fail-safe, on the other hand, is a 7-day recovery window that Snowflake provides after the Time Travel period ends. It’s meant for emergencies, like recovering data due to system issues. Unlike Time Travel, Fail-safe is not user-controlled—you need to contact Snowflake support to recover data during this period.
In short:
Time Travel = Self-service recovery (for recent changes)
Fail-safe = Last-resort recovery (handled by Snowflake support)
12 - What file formats does Snowflake support for loading data?
CSV, JSON, AVRO, ORC, PARQUET, and XML.
13 - What is Snowflake’s auto-suspend and auto-resume feature, and why is it useful?
Snowflake’s auto-suspend feature automatically pauses a virtual warehouse when it’s not being used, so it stops consuming compute resources and saves money. The auto-resume feature automatically restarts the warehouse as soon as a new query is run. This means you don’t have to manually start or stop anything—Snowflake handles it for you. It’s helpful because it reduces costs and ensures your data is always ready when needed, without wasting resources
Snowflake Interview Questions Part2 - Query Performance & Optimization
14- What are stages in Snowflake?
In Snowflake, stages are locations used to temporarily store data files before loading into tables or after unloading from tables. They act as a staging area between your local or cloud storage and Snowflake’s database tables.
Types of Stages in Snowflake
| Stage Type | Description |
| User Stage | Automatically created for each user; used to load/unload files tied to that user |
| Table Stage | Automatically created for each table; used to load files directly into that table |
| Named Stage | Manually created; can point to internal Snowflake storage or external cloud storage like S3, Azure Blob, or GCS |
15 - What are the different types of caching?
| Cache Type | What It Stores | Where It Lives | When It’s Used | Benefit |
| Result Cache | Final results of previously run queries | Cloud Services Layer | When the same query is run again with no data changes | Instant results, no compute cost |
| Metadata Cache | Table structure, file paths, stats, etc. | Cloud Services Layer | During query planning and accessing external tables | Faster query parsing and optimization |
| Data Cache | Recently accessed table data | Virtual Warehouse (Compute) | When the same data is accessed again during a session | Speeds up queries, reduces disk I/O |
16 - What is result caching?
Result caching in Snowflake helps improve performance and reduce costs by storing the results of previously executed queries. When a query is run, Snowflake saves its output. If the exact same query is executed again—and the underlying data hasn’t changed—Snowflake returns the saved result instantly from the cache, instead of reprocessing the data. This leads to faster performance, zero additional compute cost, and the ability to share cached results across users. It’s a powerful way Snowflake optimizes repeated query workloads.
17 - How to optimize a slow-running query?
Use EXPLAIN and PROFILE.
Use clustering.
Optimize joins and filters.
Ensure proper use of warehouse size.
18 - How does clustering work in Snowflake, and when should you use manual clustering?
In Snowflake, clustering is a way to organize data to make certain queries run faster. Snowflake usually handles this automatically, so most of the time you don’t need to do anything. But if you’re working with very large tables and often run queries that filter by the same column (like date or region), manual clustering can help speed things up by keeping related data close together. It’s mainly useful for improving performance on big datasets with specific query patterns
Snowflake Interview Questions Part3 - Data Warehousing Best Practices
19 - What are Snowflake schemas?
Logical structures within databases to organize tables, views, and procedures. A schema is like a folder inside a database where you store related data objects, making it easier to manage and work with your data in a clean, organized way.
20 - Difference between schema and database in Snowflake?
A schema in Snowflake is like a folder inside a database where you keep related data objects such as tables, views, and functions. It helps you organize your data in a clean and structured way, making it easier to manage, secure, and access specific sets of information within a larger database.
21 - How do you load data into Snowflake?
Use COPY INTO from internal or external stage
Via Snowpipe (for continuous loading)
Using tools like SnowSQL, ETL, or Python connectors
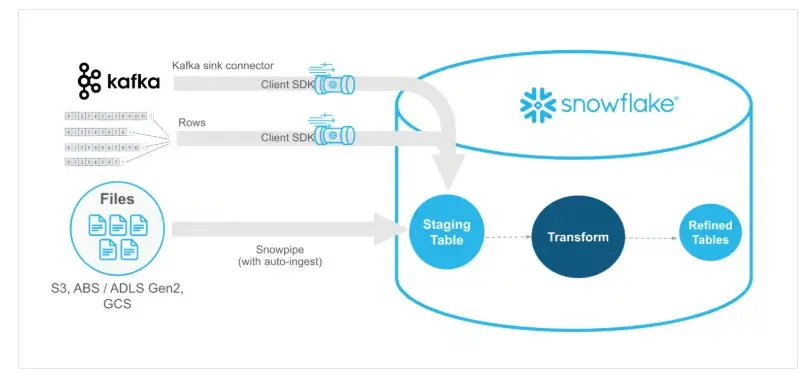
22 - What is Snowpipe?
A continuous data ingestion service that loads files automatically as they arrive in a stage.
23 - How does Snowpipe help with continuous data loading in Snowflake?
Snowpipe is a tool in Snowflake that helps load new data automatically within minutes. It works by detecting new files in a cloud storage location and loading them into a specified table in Snowflake. This happens in small batches, so the data is quickly available for use across the organization. You don’t need to manage any servers—Snowpipe takes care of the resources needed. It’s a fast, automated way to keep your data fresh and ready for analysis in near real-time.
24 - When would you use Streams & Tasks?
For incremental ELT pipelines—Streams track changes, and Tasks automate execution.
Snowflake Interview Questions Part4 - Semi-Structured & Unstructured Data
25 - Can Snowflake handle semi-structured data?
Yes. Supports VARIANT, OBJECT, and ARRAY types to handle JSON, XML, AVRO, etc.
26 - What is a VARIANT data type?
A flexible column type for storing semi-structured data—Snowflake automatically parses and optimizes it
27 - How to query JSON in Snowflake and how to flatten nested JSON arrays??
Use dot notation or `:` operator. Example: `SELECT data:name FROM my_table` where `data` is a VARIANT column.
Use the `FLATTEN()` function to explode arrays for row-level access.
28 - What all the different states of the Snowflake Virtual Warehouse.
Snowflake Virtual Warehouses can be in the following states, depending on their activity and configuration.
| State | Description |
| Running | The warehouse is active and ready to process queries or tasks. |
| Suspended | The warehouse is paused to save compute costs; it does not consume credits. |
| Resuming | The warehouse is starting up from a suspended state to become active. |
| Suspending | The warehouse is in the process of pausing due to inactivity or manual action. |
| Starting | The warehouse is being initialized (e.g., just created or resized). |
| Queued | A request to start the warehouse is waiting due to resource limits or delays. |
| Failed | The warehouse encountered an error and could not start or operate as expected. |
29 - Can Snowflake store unstructured data like images?
Yes. Snowflake supports storing and managing unstructured data in external stages using new features like Snowflake Native Apps.
Snowflake Interview Questions Part5 - Data Sharing & Collaboration
30 - What is Secure Data Sharing in Snowflake?
Secure Data Sharing in Snowflake is a feature that allows you to share data with other Snowflake accounts (or even users without an account) without copying or moving the data.
Instead of sending files or exporting data, Snowflake lets you grant access to your live data directly. The other party can query the data in real time, but they don’t actually own or store the data themselves.
32 - How does data sharing work in Snowflake, and what are the main benefits?
Snowflake allows users to share data securely and in real time without needing to copy or move it. You can share data with other Snowflake accounts or even with people who don’t have one using a feature called Reader Accounts. The main benefits are faster access, no data duplication, and better control—since the shared data always stays in your account, and you can update or remove access anytime. It’s an easy and secure way to collaborate with partners, teams, or clients.
33 - What are reader accounts?
Special accounts created by data providers to share data with consumers without requiring a Snowflake license.
34 - What is the Data Marketplace?
The Snowflake Data Marketplace is a platform where organizations can discover, access, and share live, ready-to-query data from various data providers—all within the Snowflake ecosystem
Snowflake Interview Questions Part6 - Security & Governance
35 - What are roles in Snowflake?
A role is like a set of permissions assigned to a user. For example, one role might allow someone to read data, while another lets them create or delete tables.
Key Points:
Roles are assigned to users, and roles can also be assigned to other roles (called role hierarchy).
Access to all objects in Snowflake is managed through roles.
You can create custom roles to match specific job responsibilities.
The ACCOUNTADMIN and SYSADMIN roles have the highest levels of access.
36 - What’s the difference between SYSADMIN and SECURITYADMIN?
SYSADMIN: Manages databases, warehouses
SECURITYADMIN: Manages users and roles
37 - How is data encrypted in Snowflake?
End-to-end encryption using keys managed through Tri-Secret Secure or external key management.
38 - What is row access policy?
Controls access to specific rows based on the user’s role or attribute. Helps implement fine-grained security.
39 - How can masking policies help?
Dynamic masking hides sensitive data like PII at query time based on user roles.
Snowflake Interview Questions Part7 - Advanced Topics & Real-World Scenarios
40 - What is zero-copy cloning in Snowflake, and why is it useful?
Zero-copy cloning in Snowflake lets you create a copy of a table, schema, or even an entire database instantly and without using extra storage. It doesn’t actually duplicate the data—instead, it points to the same data as the original. This makes it super fast and efficient. It’s useful because you can test changes, run experiments, or create backups without affecting the original data or paying for extra storage.
41 - How to handle CDC (Change Data Capture)?
Use Streams to capture row-level changes and process them with Tasks or ELT pipelines.
42 - What are some popular ETL tools that work well with Snowflake?
Some well-known ETL tools that are compatible with Snowflake include:
Informatica
Talend
Apache NiFi
Matillion
Fivetran
43 - What are materialized views in Snowflake, and when should you use them?
Materialized views in Snowflake are like saved query results that automatically update when the underlying data changes. Instead of running a complex query every time, Snowflake stores the results so they can be accessed quickly. This makes it faster to get answers from large or repeated queries. They’re great for dashboards, reports, or any case where performance matters and the data doesn’t change too often.
44 - Difference between View and Materialized View?
| Feature | View | Materialized View |
| Data Storage | Doesn’t store data; runs the query each time | Stores the query result for faster access |
| Performance | Slower for complex or repeated queries | Faster, especially for large and frequent queries |
| Data Freshness | Always shows the most up-to-date data | May have a small delay as it refreshes automatically |
| Use Case | Good for light or rarely used queries | Ideal for dashboards and frequent data access |
| Maintenance | No extra cost or upkeep | Slightly more storage cost; Snowflake maintains it |
45 - How do shared-disk and shared-nothing architectures differ?
In a shared-disk architecture, all the servers (or nodes) share the same storage. Each server can access all the data, which makes it easier to manage, but it can also lead to performance issues if many servers try to use the same disk at once.
In a shared-nothing architecture, each server has its own storage and memory. They work independently, which reduces traffic and improves performance. This setup is great for scaling out, since adding more servers increases both compute and storage power without conflicts.
In short:
Shared-disk = Easier to manage, but can get slow with heavy use.
Shared-nothing = Faster and more scalable, with each server working on its own.
46 - What is Snowpark?
A developer framework allowing data engineering and ML tasks using Python, Java, or Scala directly in Snowflake.
48 - Explain Task Scheduling.
Use Tasks to automate SQL statements on a schedule or after an event, ideal for pipeline orchestration.
49 - How to monitor Snowflake usage?
Via Account Usage Views, Query History, and WAREHOUSE_LOAD_HISTORY.
50 - How to manage cost in Snowflake?
Auto-suspend warehouses
Use correct warehouse sizes
Monitor with usage views and alerts
51 - What is a multi-cluster warehouse?
A warehouse that scales horizontally to handle concurrent users without queueing.
Snowflake Interview Questions Part8 - Interview Strategy & Thought Process
52 - How would you explain Snowflake to a non-technical stakeholder?
It’s like a cloud-based Excel that can handle massive data, is always fast, and doesn’t need IT to maintain.
53 - What’s your favorite feature in Snowflake and why?
Good to choose answer like Zero-Copy Cloning—great for sandbox testing without additional cost or time.
54 - When would you choose Snowflake over BigQuery or Redshift?
When you need multi-cloud, cross-region data sharing, high concurrency, and simplified management.
55 - How does Snowflake support both ETL and ELT data processing methods?
Snowflake supports both ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) approaches. With ETL, you clean and transform the data before loading it into Snowflake. With ELT, you load raw data into Snowflake first and then use its powerful SQL engine to transform it. Snowflake’s flexibility, scalability, and strong processing power make it easy to use either method, depending on what works best for your data workflows.
56 - How do you ensure data quality in Snowflake pipelines?
Use Constraints and Validations
Audit logs via Account Usage views
Profile data using custom scripts
57 - Have you ever optimized a Snowflake workload?
Yes—replaced large queries with materialized views and introduced clustering on time-based data.
58 - What would you improve in Snowflake?
Integration with orchestration tools like Apache Airflow or native alerting for anomaly detection.
59 - How does Snowflake handle both OLTP and OLAP workloads?
Snowflake is mainly designed for OLAP (Online Analytical Processing), which means it’s great for analyzing large amounts of data, running complex queries, and generating reports. It’s not built for traditional OLTP (Online Transaction Processing) tasks like frequent small updates or real-time transactional systems. However, Snowflake can handle some light OLTP-like workloads, especially when paired with modern tools. Its strength lies in fast, large-scale data analysis rather than high-speed transaction processing.
60 - How does Snowflake handle both OLTP and OLAP workloads?
Snowflake is mainly designed for OLAP (Online Analytical Processing), which means it’s great for analyzing large amounts of data, running complex queries, and generating reports. It’s not built for traditional OLTP (Online Transaction Processing) tasks like frequent small updates or real-time transactional systems. However, Snowflake can handle some light OLTP-like workloads, especially when paired with modern tools. Its strength lies in fast, large-scale data analysis rather than high-speed transaction processing.
Final Thought
Mastering Snowflake interview questions isn’t just about memorizing facts—it’s about understanding the platform’s real-world value. Whether it’s query optimization, secure data sharing, or designing resilient ELT pipelines, recurring themes include automation, scalability, and simplicity.
Preparation is your best asset—use this guide as a launchpad and pair it with hands-on practice to build true confidence. Interviews test not only what you know but how you apply it.
Snowflake Resources : Snowflake University, Snowflake Documentation
Visit ByteandStar Education for more interview questions.

Some really nice stuff on this web site, I like it.
Thank you so much! I’m really glad you liked it 😊 Your appreciation truly means a lot!
some genuinely prize posts on this web site, saved to my bookmarks.
Thank you so much, appreciate your feedback.